Lab 04 : Selection in Flowgorithm
Implementing Selection
Selection in flowchart is represented by the diamond shape. In Flowgorithm, it is the same. Before we start using the diamond shapes, lets use one example from Tutorial 3 for us to implement in Flowgorithm
MyHealth magazine is sold at RM5.00 each if at least 5 units of the magazine are purchased, and it is sold at the price of RM7.00 each otherwise. Calculate the price a customer has to pay after they enter the quantity of the magazines that they purchased.
Lets skip the Input shape and Declare shape for the questions, if you forgot how to do that, you can refer back here.
After declaring input and accepting input from the user, you will got this
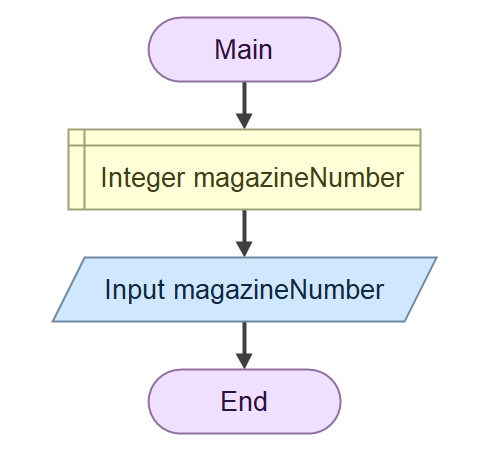
You have one input, the magazinesNumber.This is a simple selection (if–else) problem: if magazinesNumber ≥ 5, the unit price is RM5.00. Otherwise, the unit price is RM7.00. Note the boundary case that "at least 5" , so you must includes 5.
Now that we have establish the structure of the algorithm, we have discovered a new variable, which is unitPrice. Declare the variable using the Declare shape just under the input.
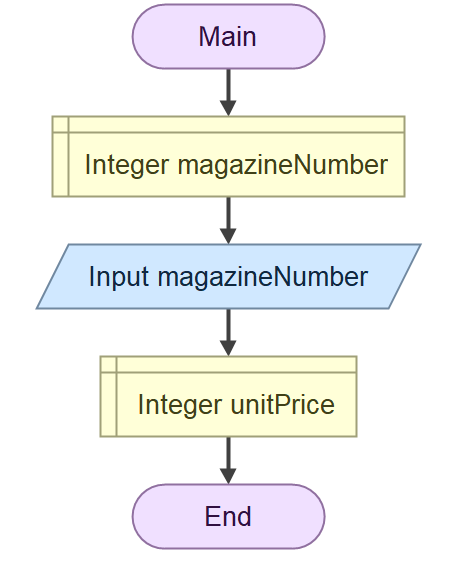
The selection will be added after the unitPrice have been declared, The reason we did this is so that we only need to declare it once. If we declared the variable after the selection, we will have to declare it two times, one after the True condition and one after the False condition.
To add the selection, click the arrow underneath unitPrice and a popup window will open. Under the Control section, click the Diamond shape.
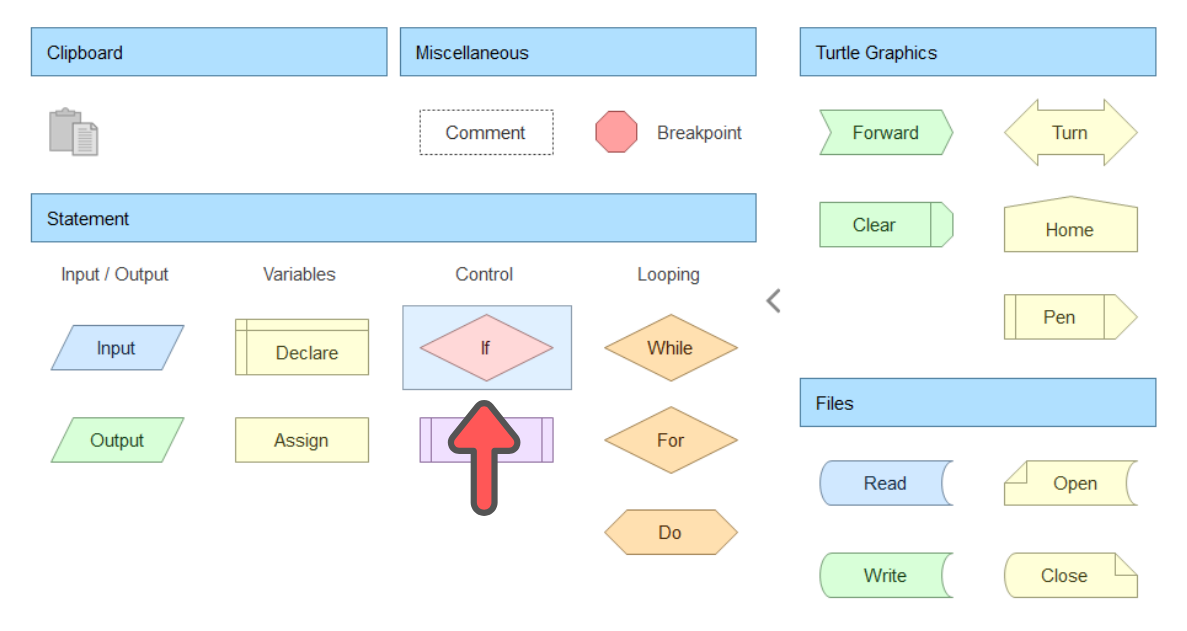
The Diamond shape will automatically have two arrow coming out of them. The left one is for false and the right one for true.
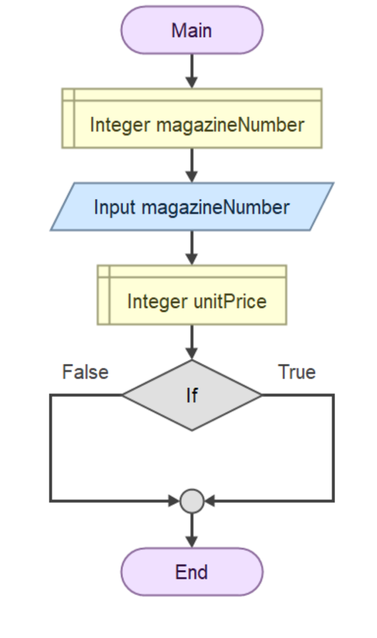
Double click the Diamond shape and a popup window will appear that will prompt you to enter condition of the expression. For our questions, we will enter magazineNumber >= 5 as our condition.
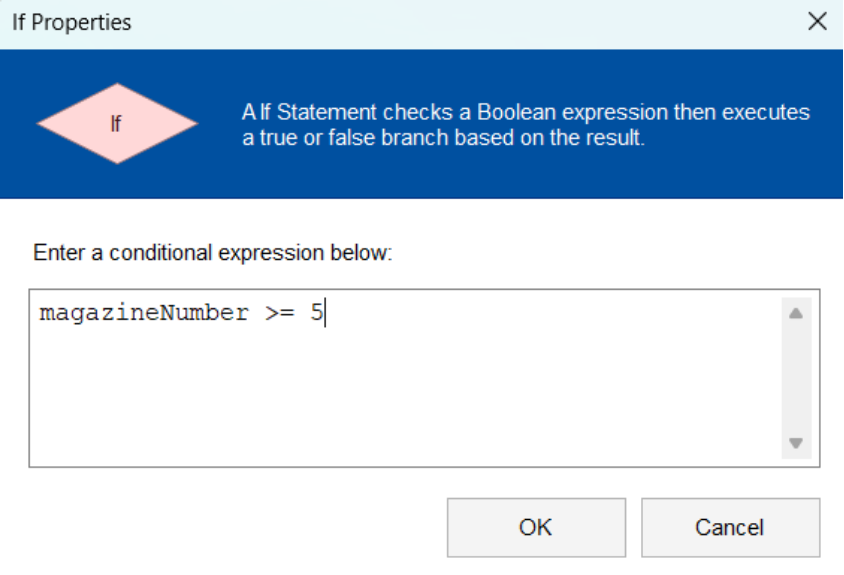
NOTE
Only variable that have been declared can be used in the conditions. Make sure you declared all the necessary variable that you are going to need. Any condition inside the Diamond must be either evaluated to True or False.
Now we need to add the logic for both paths of the selection:
True Path (Right Side): If magazineNumber >= 5 is True, this means the customer is buying 5 or more magazines, so they get the discounted price. We need to set unitPrice = 5.
False Path (Left Side): If magazineNumber >= 5 is False, this means the customer is buying fewer than 5 magazines, so they pay the regular price. We need to set unitPrice = 7.
Click on the True arrow (right side) and add an Assign shape. Set the assignment to unitPrice = 5.
Click on the False arrow (left side) and add an Assign shape. Set the assignment to unitPrice = 7.
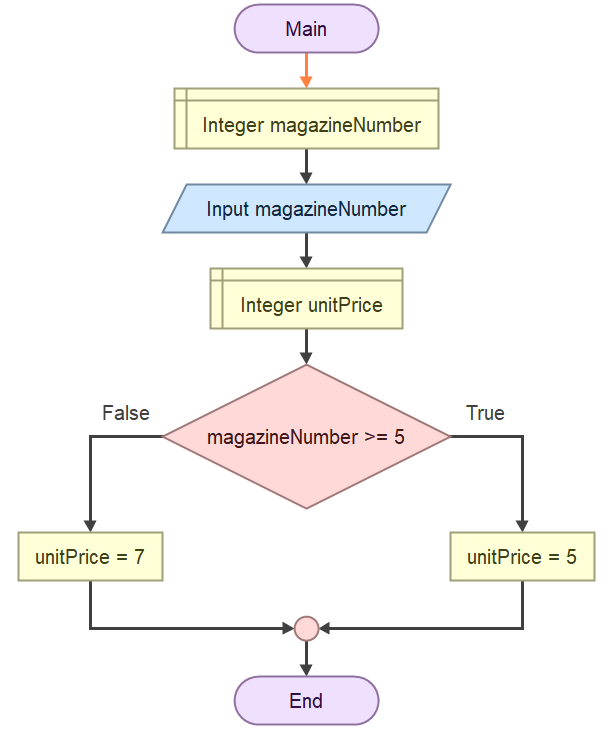
After both paths, the flowchart will merge back together (note the circle connector in the image), and you can continue with calculating the total price by multiplying unitPrice with magazineNumber.
After the selection structure, we need to complete the flowchart. First, declare a new variable called finalPrice using the Declare shape to store the calculated total cost.
Next, add an Assign shape to calculate the final price using the formula finalPrice = magazineNumber * unitPrice. This will multiply the number of magazines by the unit price we determined from the selection.
Finally, add an Output shape to display the finalPrice to the user.
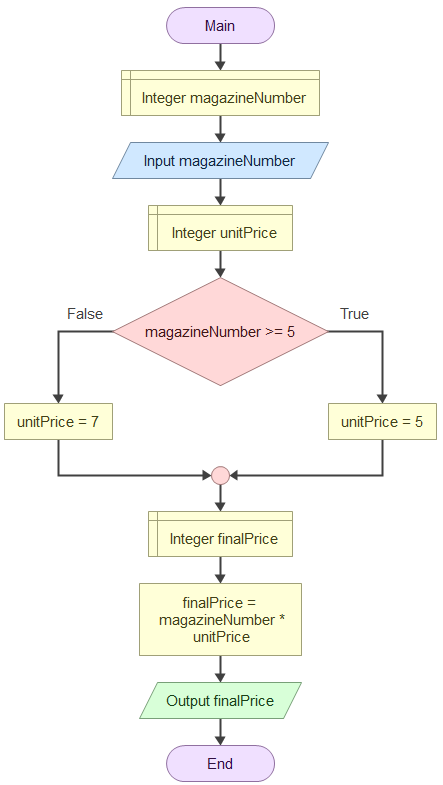
The complete flowchart shows how the selection structure works:
- The diamond shape evaluates the condition
magazineNumber >= 5 - If True (right path):
unitPrice = 5 - If False (left path):
unitPrice = 7 - Both paths merge back together at the circle connector
- Then the final calculation and output steps are executed
Exporting Flowgorithm to Image
At the top bar, click Tools > Export to an Image file.
After you click it, a popup window will appear, no need to change anything and just click Create atthe bottom right of the window.
Then it will prompt you the location that you want the image saved and the name of the image. Rename the image to lab-4-1.
Selection Questions
Scenario 1 - Electricity Bill Question
A utility company charges RM0.30 per kWh for the first 100 kWh, RM0.50 per kWh for the next 100 kWh (101–200 kWh), and RM0.75 per kWh for any usage above 200 kWh.
Calculate the total bill when the customer enters their total kWh consumed.
Scenario 2 - Income Tax Slab Question
Income tax is applied as:
First RM50,000.00 → 0%
Next RM50,000.00 → 1%
Above RM100,000.00 → 2%
Given an annual income, calculate total tax due.
Scenario 3 - Parking Fee Question
A mall charges parking as follows:
First 2 hours → Free
Next 3 hours (2–5 hours) → RM2.00 per hour
Beyond 5 hours → RM3.00 per hour
Maximum charge per day → RM30.00
Given total hours parked, calculate the parking fee.
Scenario 4 - Baggage Allowance Logic Question
A flight ticket that includes 15 kg of free baggage.Excess baggage is charged RM4.00 per kg beyond that limit. However, if the passenger brings no baggage, they receive a RM10.00 discount on the total ticket price.
Given the weight of baggage and ticket price, calculate the final price.